Companies have many questions around how data will be integrated between cloud and on-premise applications, how data migration and data quality can be addressed while moving from existing SAP or non-SAP systems to S/4HANA or other future applications, what is the best way to manage data in data warehouse and data mart and finally which tool to select for different use case for data integration.
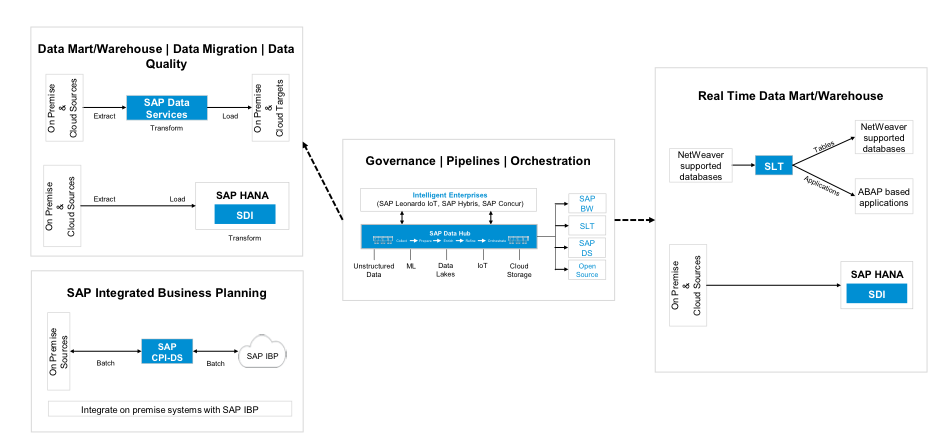
SAP has several data integration tools like SAP Data services, SAP Cloud platform integration for data services, SAP Hana smart data integration, SAP Cloud platform smart data integration, SAP Landscape Transformation Replication Server and Data Hub to integrate data. Below snapshot gives the overview of all these tools and when to use what:
1. SAP data services
SAP Data Services empowers IT users to easily integrate, transform, improve, and deliver accurate and complete data to support operational and analytical data-driven initiatives.
Scope and purpose of SAP data services can be categorized in four steps.
- It accesses, and extracts structured and unstructured data from SAP and non-SAP systems in batch or real-time.
- It transforms, cleanse, match and consolidate data.
- It supports wide variety of SAP and non-SAP targets
- It has data quality check functions for address validation, duplicate records and geocode search.
When should I use SAP Data Services:
- Data migration: It can be used to migrate data from SAP or non-SAP OLTP systems to target SAP OLTP system.
- Data warehouse and Data marts: It can be used to analyze the condition of data sources in OLTP and extract, integrate and cleanse data to OLAP target in batch loads.
- System landscape: It is on-premise deployment and it is used to connect many sources to many targets.
2. SAP Cloud platform integration for data services
Cloud Platform Integration for data services is a cloud-based data integration tool for batch data integration between on premise applications and cloud applications.
Scope and purpose of SAP Cloud platform integration for data services can be categorized in below steps.
- It can access on premise SAP ECC, S/4 HANA and APO data sources or 3rd party databases through an on-premise agent.
- It is co-located with the HANA database in the cloud for direct data loads at HANA database level.
- It supports Bi-directional data transfer.
- It performs batch loads with built-in scheduler for ETL jobs.
- It offers Out-of-the-box content and flexible web-based UI to customize dataflows.
- Data never persists in cloud as it is piped.
When should I use SAP Data Services:
SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP) uses SAP Cloud Platform Integration for data services for integration with on-premise applications.
3. SAP HANA smart data integration and SAP Cloud Platform Smart Data Integration
SAP HANA smart data integration and SAP Cloud Platform Smart Data Integration delivers real-time data integration and transformation capabilities as part of the SAP HANA platform. SAP HANA SDI is for HANA centric on-premise systems and SAP Cloud Platform SDI is for integration of on-premise systems with SAP Cloud Platform.
Scope and purpose of SAP HANA SDI can be categorized in four steps.
- It delivers real time data integration. Virtualization capability allows to release the data once transaction is completed.
- It is built in HANA platform so if one has HANA platform then one gets SAP HANA SDI as part of it.
- It is ELT tool as it extracts, load to HANA then transform. It can be used to get data out of HANA, but it is not recommended.
- Data quality can be performed with help of SDQ.
One major difference between SAP HANA SDI and SAP Cloud Platform SDI is that SAP Cloud Platform SDI does not do data quality as address directory can be not deployed but there are APIs for geo and address validation.
When should I use SAP HANA SDI and SAP Cloud Platform SDI:
- Data migration: It can be used to migrate data from SAP or non-SAP OLTP systems to target SAP OLTP system.
- Data warehouse and Data marts: It is used to integrate data from OLTP, file and social media to OLAP in batch or real time.
- System landscape: SAP HANA SDI and SAP Cloud Platform SDI are for HANA centric system landscapes
4. SAP Landscape Transformation Replication Server
SAP Landscape Transformation Replication Server (aka SLT) is a real time, trigger-based, data replication solution from ABAP and non-ABAP sources for SAP NetWeaver supported databases only.
Scope and purpose of SLT can be categorized in below steps.
- It provides replication staging for high availability and disaster recovery.
- It has transformational and filter capabilities.
- It provides application-based and table-based replication.
- It offers real time and batch data integration.
When should I use SLT:
- Data warehouse and Data marts: It can be used for near real time data acquisition to SAP Business Warehouse, for SAP HANA data marts and data warehouse.
- System landscape: Target landscape could be HANA or non-HANA centric.
Applications: It can be used for to replicate real time data from SAP ERP on anyDB for S/4HANA Central Finance, fraud management, CO/PA and etc.
5. SAP Data Hub
SAP Data Hub enables the intelligent enterprise by providing an all-in-one data management solution that governs, integrates, processes and orchestrates enterprise and big data in on premise, cloud, multi-cloud and hybrid distributed system landscapes.
Scope and purpose of SLT can be categorized in below steps.
- It provides integration between enterprise application like SAP S/4HANA, SAP Hybris, SAP BW/4HANA and etc.
- It comes with predefined content to integrate application.
- It establishes big data centric architecture with open source and 3-party integration.
- All other SAP data integration tools are for data integration but SAP Data Hub is a tool for integration, governance, processing and orchestrating enterprise and big data.
When should I use SLT:
- System landscape: It can be used for cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP), on-premise, hybrid and multi cloud centric system landscapes.
- Machine learning and predictive analytics: It has ML/AI and data science models to support ML and predictive capabilities.
Below is the summary of all above data integration tools used for different use cases.